Tubal Pregnancy (Ectopic Pregnancy)
Definition
Any pregnancy where the fertilized ovum gets implanted and develops in a site other than normal uterine cavity
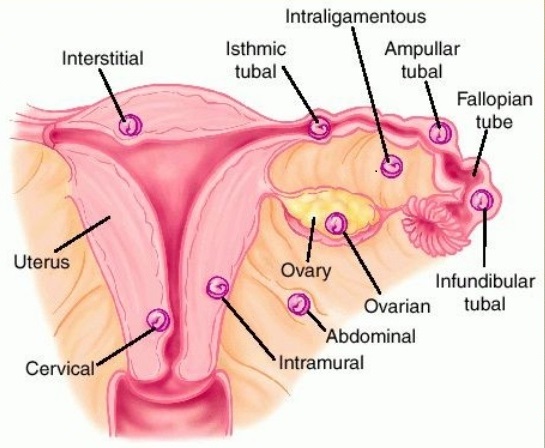
Implantation Sites
Extrauterine : Tube - ampulla 70%, isthmus, infundibulum cornual
Extra uterine : abdominal : Intraperitoneal, extraperitoneal
Uterine : cervical, angular, cornual, caesarian scar
Etiology
Delayed transport through tube
Congenital: tubal hypoplasia, tortuosity, congenital diverticuli, accessory ostia, partial stenosis, elongation, intramural polyp,
Acquired defects of the tube: PID (Chlamydia trachomatis),
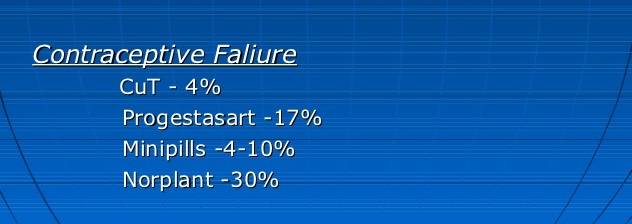
Contraceptive failure, tubal sterilization failure,
Use of emergency contraception in current pregnancy
Conception whilst using POP
reversal of sterilization
Age 35 - 45
Previous induced abortion
Previous Pelvic or tubal surgery
Smoking
Salpingitis isthmica nodosa
Genital tuberculosis
Fundal fibroid
Adenomyosis of the tube
Transperitoneal migration of ovum
Tubal endometriosis
Previous ectopic pregnancy
H/O infertility or assisted conception, Infertility treatments such as IVF
Smoking
Sexually transmitted diseases
Unsuccessful tubal ligation or tubal ligation reversal
Use of fertility drugs
Incidence
Increased due to PID, IUCD, Tubal surgeries, Assisted reproductive techniques (ART)
Ranges from 1:5 to 1:250
Late marriage
Late child bearing
Recurrence rate : 15% after the first ectopic pregnancy and 25% after 2nd
Symptoms and signs
pain, amenorrhoea, vaginal spotting or bleeding
Abdominal pain - diffuse - association with vomiting - pain lasting for more than 30 minutes and flashing
Nausea and vomiting with pain
Sharp abdominal cramps
Pain on one side of the body
Dizziness or weakness
Pain in the shoulder, neck or rectum
Vaginal bleeding
Abnormal period where bleeding is prolonged with 'brown juice' spotting
Patient may not be aware of pregnancy
Shoulder tip pain - (hemoperitoneum irritating the diaphragm)
Sometimes only mild discomfort or diarrhoea
Early diagnosis → wider choice of management options, potentially decreasing morbidity and mortality
Diagnosis
The clinician should have a high index of suspicion
Pregnancy test
Pelvic examination
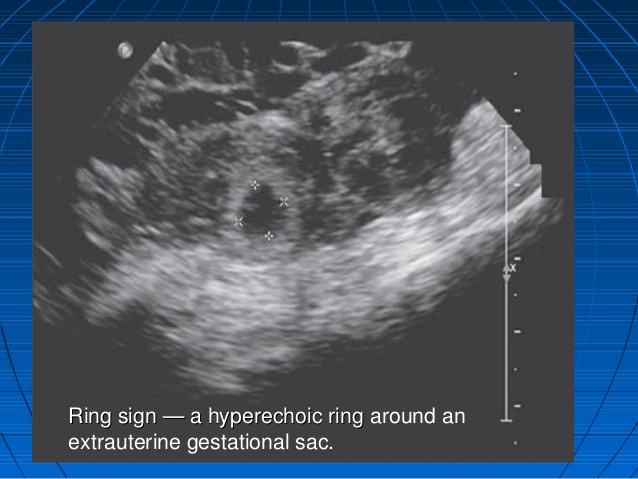
USGM:- a gestational sac with fetal heart in the fallopian tube seen. Transvaginal USGM: sensitivity of at least 90%.
Estimation Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin
Hb, TC, DC, blood grouping & cross matching, BT, CT
Culdocentesis through posterior fornix 0.5 ml of non clotting blood is a +ve test
Color Doppler sonography (TV-CDS)
Serum progesterone
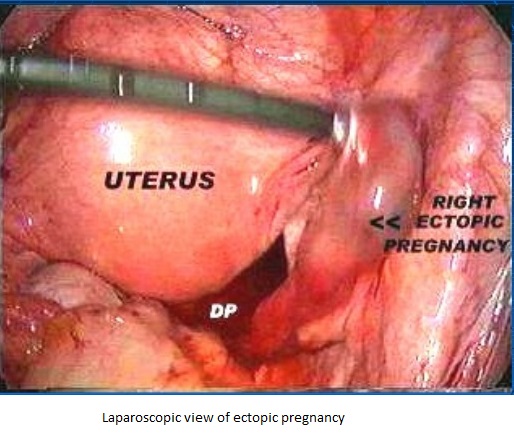
Diagnostic Laparoscopy : Gold standard
Differential Diagnosis
Rupture of corpus luteum of pregnancy
Rupture of chocolate cyst
Twisted ovarian cyst
Torsion/degeneration of pedunculated fibroid
Incomplete abortion
Acute appendicitis
Perforated peptic ulcer
Renal colic
Splenic rupture
DD of subacute ectopic pregnancy : -
Pelvic abscess
Pyosalpinx
Subserous uterine uterine fibroid
Salpingitis
Retroverted gravid uterus
Appendicular lump
Treatment
Medication : very early - Methotrexate
Surgery : Laparoscopy :
Radical saplingectomy
Salpingostomy
Salpingotomy
Segmental resection
Milking of fimbria and expression
Supprtive measures like IV fluids, blood, combating shock
Complications
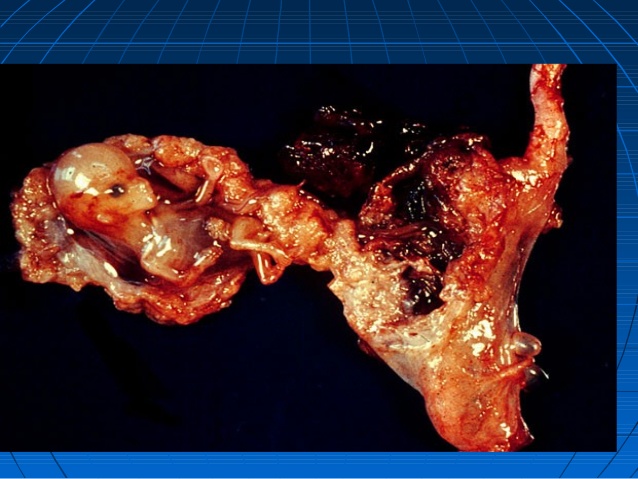
Fallopian tube rupture - hemoperitoneum and attendant events including shock
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
The combination of sensitive urinary pregnancy tests, transvaginal ultrasound and serum hCG estimations enables the early diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy in modern clinical practice. However, the diagnostic accuracy and sensible application of these tests relies on good basic clinical skills. There is no substitute for eliciting a clear history and taking the woman’s symptoms and signs into account.
The incidence of ectopic pregnancy is about 1-3%, depending on the population studied. 95-97% of ectopic pregnancies are tubal pregnancies.
Ectopic pregnancies are classified as follows: